2nd order Nonhomogeneous Differential Equation MKMath
It's now time to start thinking about how to solve nonhomogeneous differential equations. A second order, linear nonhomogeneous differential equation is. y′′ +p(t)y′ +q(t)y = g(t) (1) (1) y ″ + p ( t) y ′ + q ( t) y = g ( t) where g(t) g ( t) is a non-zero function. Note that we didn't go with constant coefficients here because.
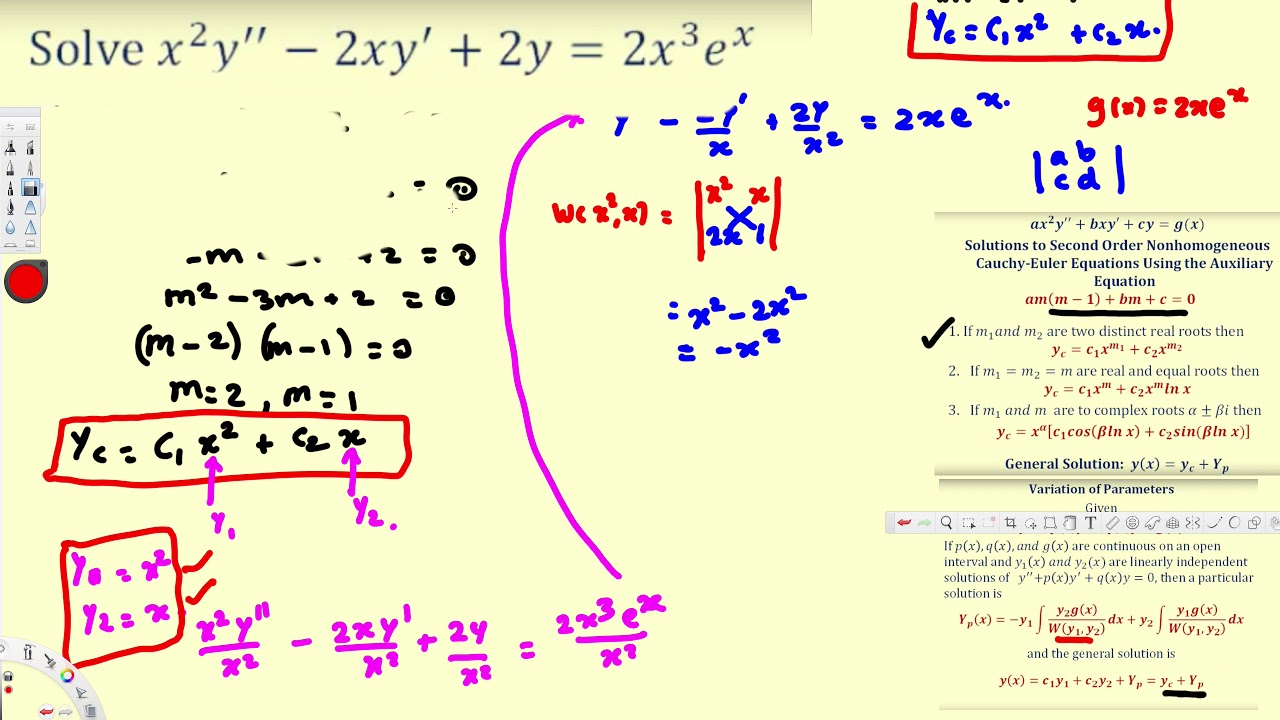
Second Order Nonhomogeneous Cauchy Euler Differential Equations YouTube
Consider the nonhomogeneous linear differential equation \[a_2(x)y″+a_1(x)y′+a_0(x)y=r(x). \nonumber \] The associated homogeneous equation \[a_2(x)y″+a_1(x)y′+a_0(x)y=0 \nonumber \] is called the complementary equation. We will see that solving the complementary equation is an important step in solving a nonhomogeneous differential.
Solved A nonhomogeneous 2ndorder differential equation is

The formal definition is: f (x) is homogeneous if f (x.t) = t^k . f (x), where k is a real number. It means that a function is homogeneous if, by changing its variable, it results in a new function proportional to the original. By this definition, f (x) = 0 and f (x) = constant are homogeneous, though not the only ones.
Particular Solution of NonHomogeneous Differential Equations

3.3 Nonhomogeneous Linear Second-order Differential Equations A. General Solution of Nonhomogeneous Equations. In this section, we explore the nonhomogeneous linear second-order differential equation of the form:
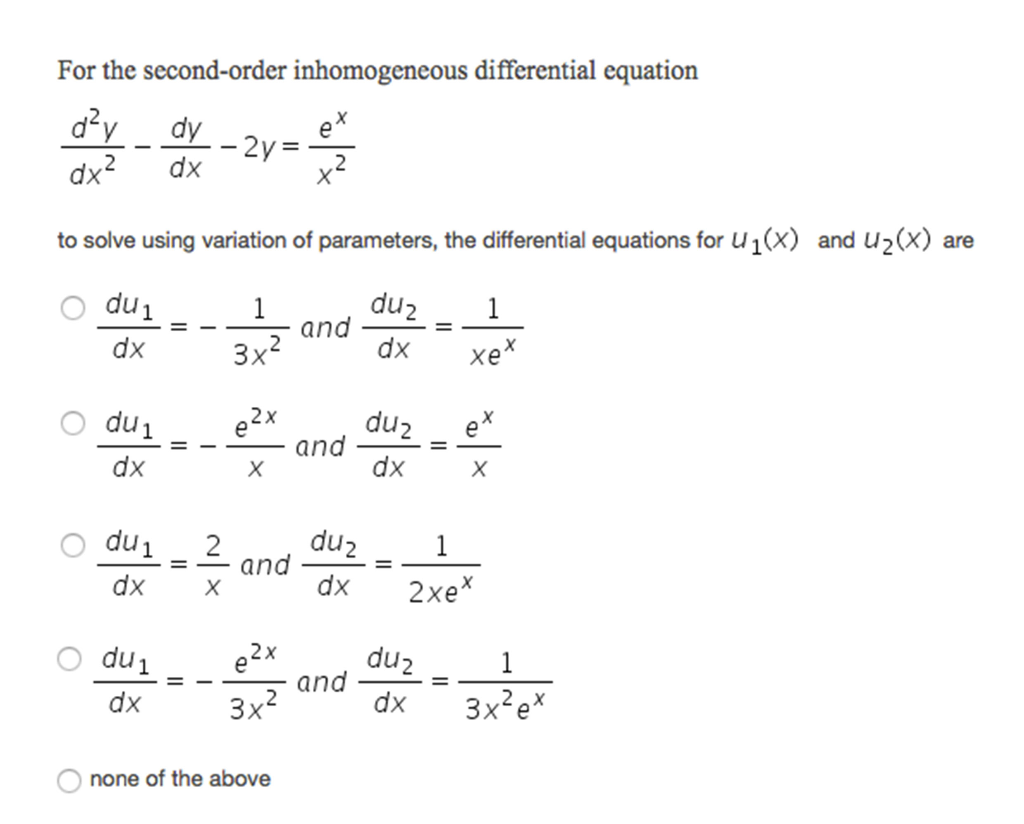
Solved For the secondorder inhomogeneous differential
We know from Additional Topics: Second-Order Linear Differential Equationshow to solve the complementary equation. (Recall that the solution is , where and are linearly independent solutions of Equation 2.) Therefore, Theorem 3 says that we know the general solution of the nonhomogeneous equation as soon as we know a par-ticular solution .
Solved Topic 3. Second order, nonhomogeneous differential

Let the general solution of a second order homogeneous differential equation be. Instead of the constants and we will consider arbitrary functions and We will find these functions such that the solution. satisfies the nonhomogeneous equation with the right side. The unknown functions and can be determined from the system of two equations:
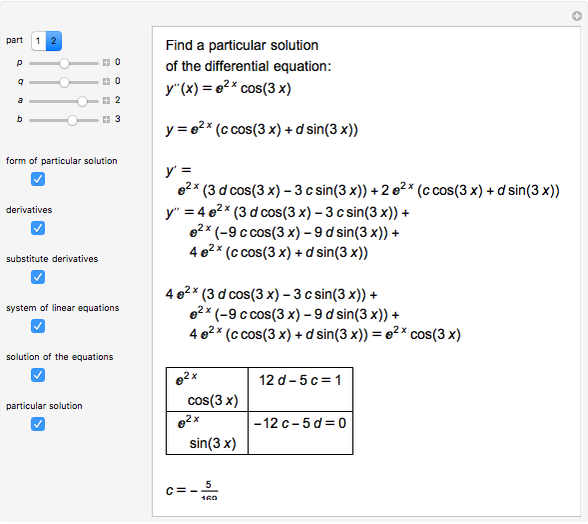
Particular Solution of a Nonhomogeneous Linear SecondOrder Differential Equation with Constant
So if this is 0, c1 times 0 is going to be equal to 0. So this expression up here is also equal to 0. Or another way to view it is that if g is a solution to this second order linear homogeneous differential equation, then some constant times g is also a solution. So this is also a solution to the differential equation.
Solving a SecondOrder Nonhomogeneous ODE with Constant Coefficients IVP (Example) YouTube

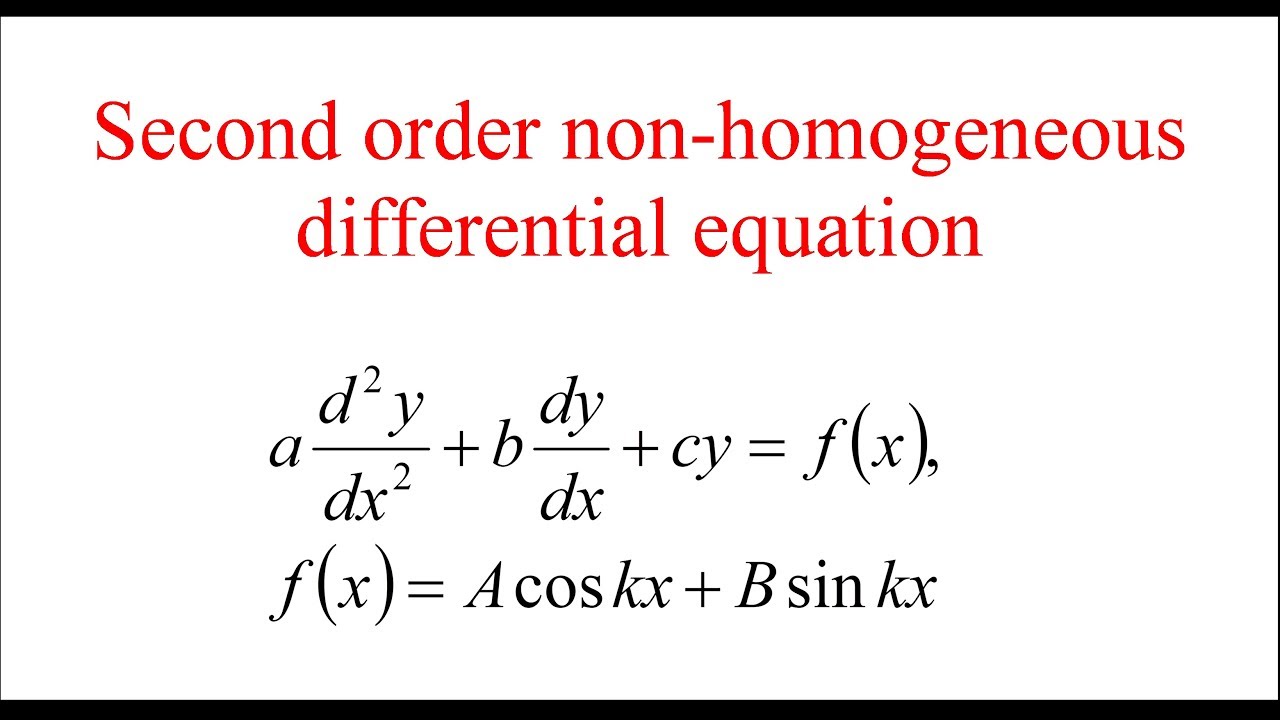
17.2: Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations. Now we consider second order equations of the form ay¨ + by˙ + cy = f(t), with a, b, and c constant. Of course, if a = 0 this is really a first order equation, so we assume a ≠ 0. Also, much as in exercise 20 of section 17.5, if c = 0 we can solve the related first order equation ah˙ + bh = f(t), and.
Variation of parameters Solving Nonhomogeneous Second Order Differential Equations YouTube

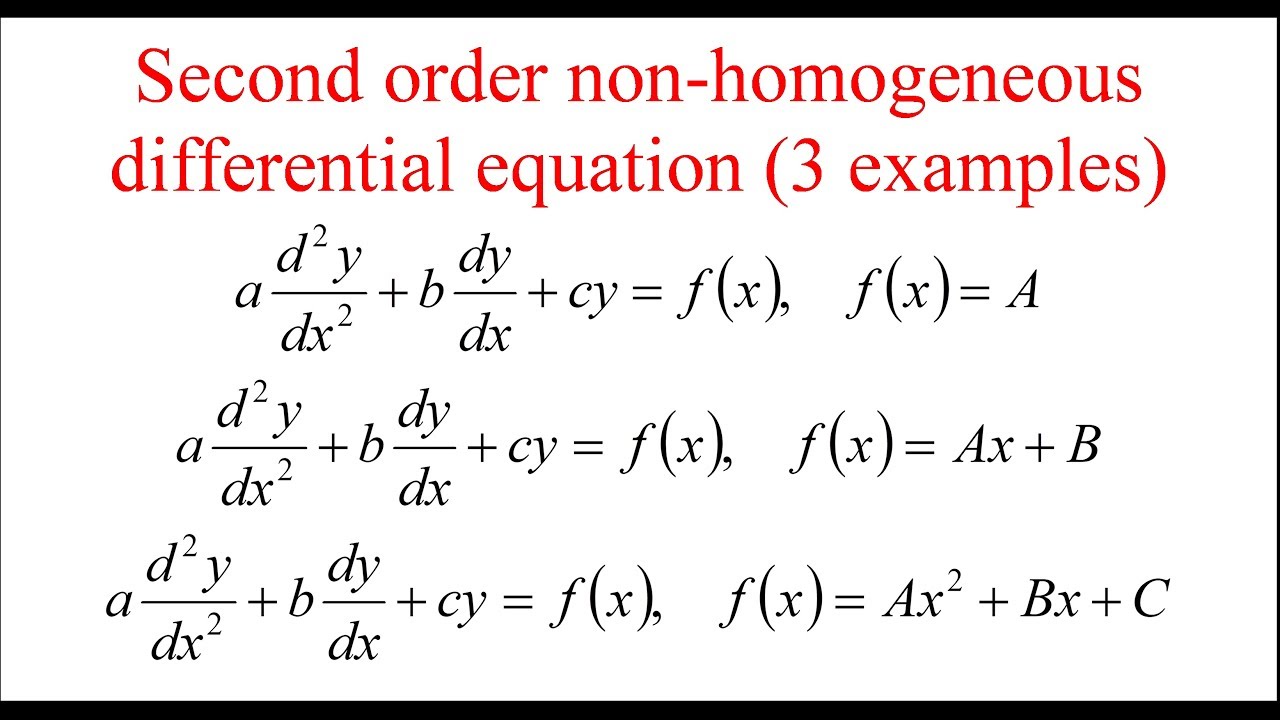
Example 2. Find the general solution of the non-homogeneous differential equation, y ′ ′ ′ + 6 y ′ ′ + 12 y ′ + 8 y = 4 x. Solution. Our right-hand side this time is g ( x) = 4 x, so we can use the first method: undetermined coefficients.
Second Order Non Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations with ics Q10 YouTube

Second Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients: a2y ′′(t) +a1y′(t) +a0y(t) = f(t), where a2 6= 0 ,a1,a0 are constants, and f(t) is a given function (called the nonhomogeneous term). General solution structure: y(t) = y p(t) +y c(t) where y p(t) is a particular solution of the nonhomog equation, and y
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 2nd Order NonHomogenous Equation Linear Function Particular Solution
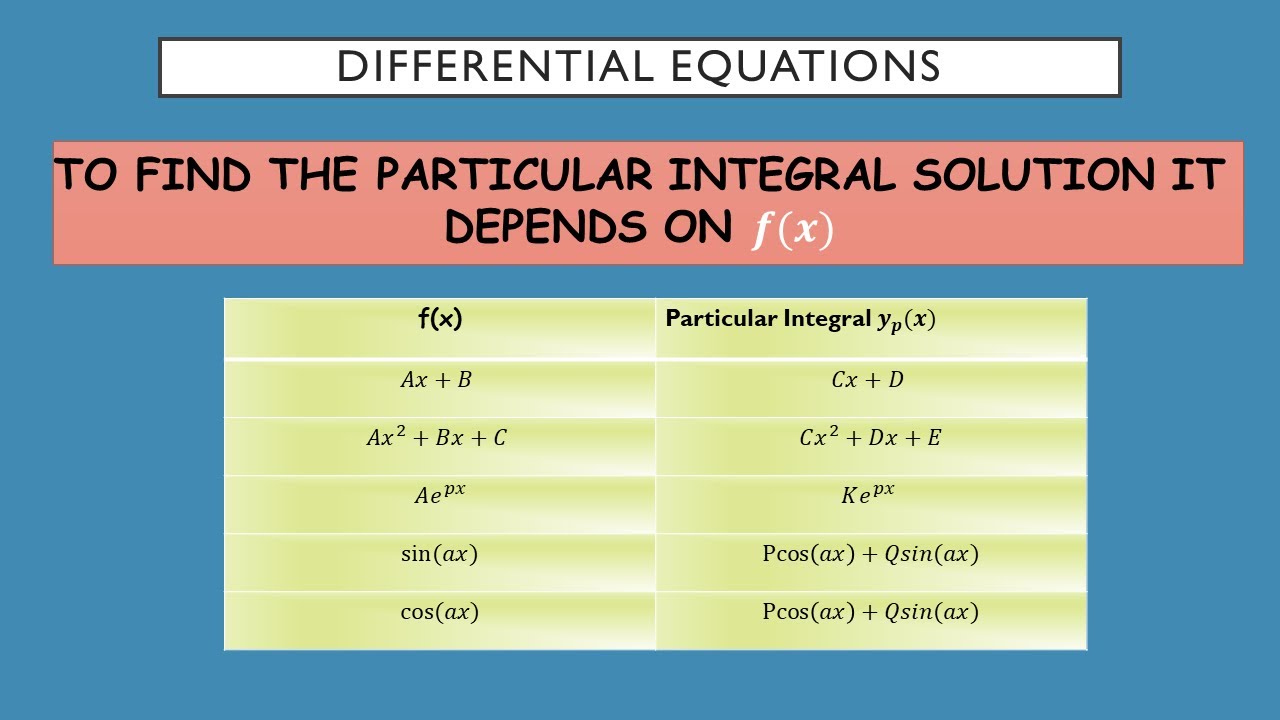
7 Second-Order Differential Equations. Introduction; 7.1 Second-Order Linear Equations; 7.2 Nonhomogeneous Linear Equations; 7.3. functions, sines, and cosines. So when r (x) r (x) has one of these forms, it is possible that the solution to the nonhomogeneous differential equation might take that same form. Let's look at some examples to.
Solving NonHomogenous Second Order Differential Equations YouTube

In this section we will work quick examples illustrating the use of undetermined coefficients and variation of parameters to solve nonhomogeneous systems of differential equations. The method of undetermined coefficients will work pretty much as it does for nth order differential equations, while variation of parameters will need some extra derivation work to get a formula/process we can use.
Second order non homogeneous differential equation YouTube
Learning Objectives. 7.1.1 Recognize homogeneous and nonhomogeneous linear differential equations.; 7.1.2 Determine the characteristic equation of a homogeneous linear equation.; 7.1.3 Use the roots of the characteristic equation to find the solution to a homogeneous linear equation.; 7.1.4 Solve initial-value and boundary-value problems involving linear differential equations.
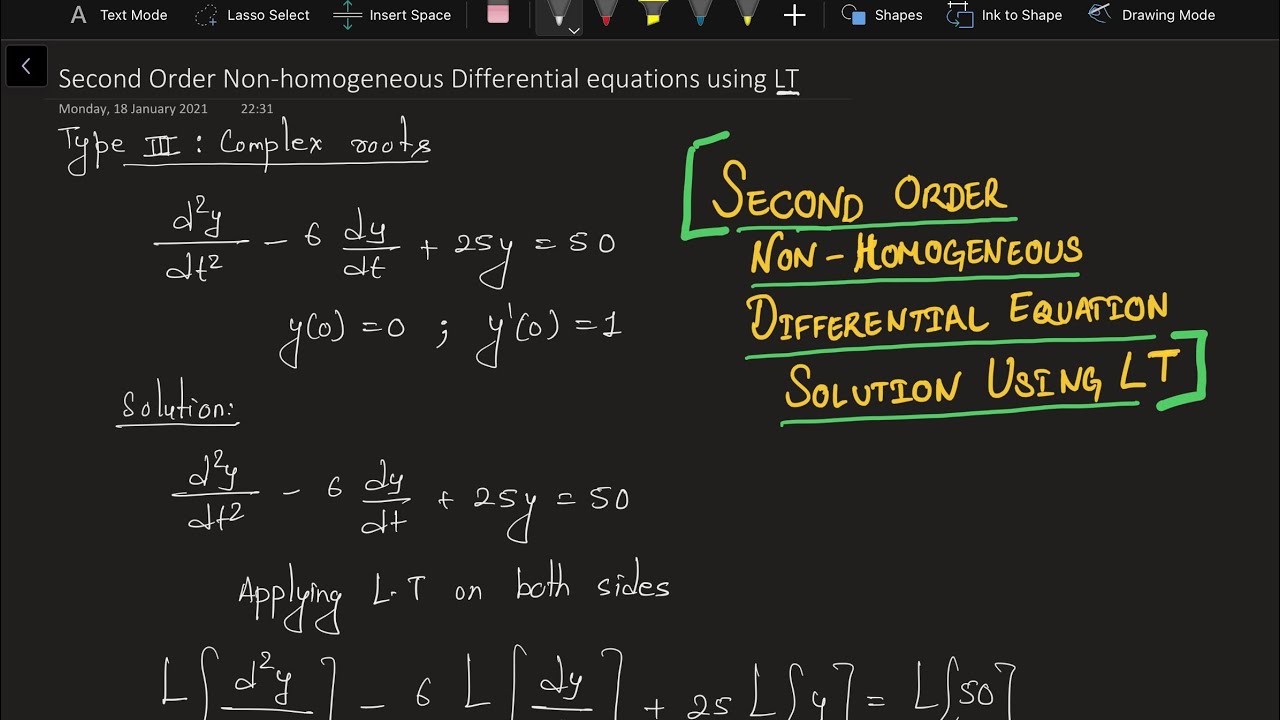
2nd Order Non homogeneous Differential Equation Solution using Laplace Transform Complex Roots
To solve a nonhomogeneous linear second-order differential equation, first find the general solution to the complementary equation, then find a particular solution to the nonhomogeneous equation. Let yp(x) y p ( x) be any particular solution to the nonhomogeneous linear differential equation a2(x)y′′+a1(x)y′+a0(x)y = r(x) a 2 ( x) y.
SecondOrder NonHomogeneous Differential Equations 2 (KristaKingMath) YouTube

Undetermined coefficients is a method you can use to find the general solution to a second-order (or higher-order) nonhomogeneous differential equation. Remember that homogenous differential equations have a 0 on the right side, where nonhomogeneous differential equations have a non-zero function on the right side.
Second order nonhomogeneous differential equation YouTube
How to solve a second-order nonhomogeneous linear differential equation with constant coefficients? The example of a mass at the end of a vibrating string is used taking into account spring force, damping force and an external force. Math-Explained by TU Delft OpenCourseWare is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial.